Abstract
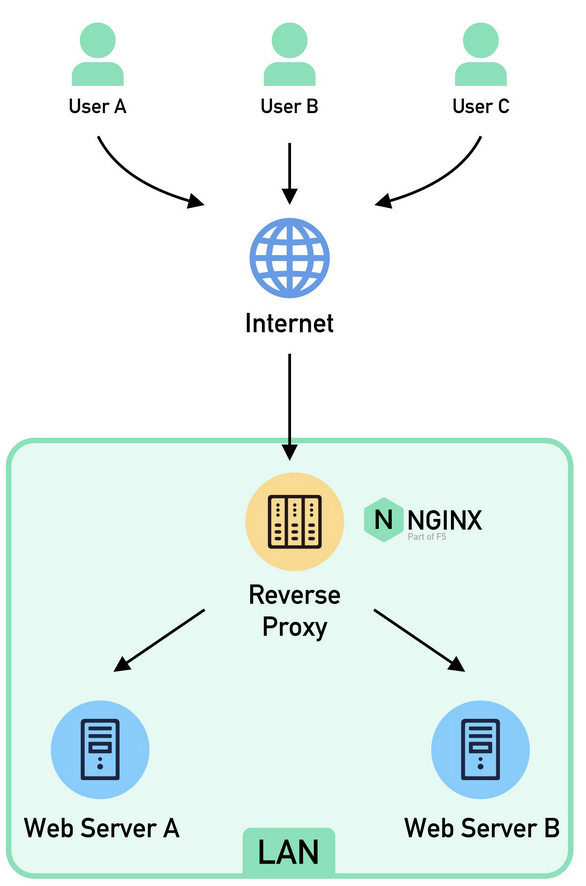
- Sits between Internet and Server that accepts a request from the Client, forwards the request to server, and returns the results to the client as if the proxy server had processed the request
- The client doesn’t know which destination server it is connecting to. However, some can add HTTP Headers to tell the client which destination server it is connecting to
- We can have multiple layers of Reverse Proxy between the client and server to form a Ingress Service
- For traffic that is coming in
Benefits
Load Balancing
- Distribute traffic from all clients to servers evenly to prevent any single server from overloading
Protection Against DDoS
- IP Address of Servers is hidden behind Reverse Proxy from clients
- And reverse proxy is usually a cluster of many many servers that can share the DDoS traffic
Cache Static Content
- The static content can be cached at the reverse proxy
- This removes some load from the servers and it is faster for the client to get back the requested resources
Handles SSL Termination
- Since the reverse proxy sits within the same trusted network as the server
- We can perform SSL Termination on the reverse proxy, so the server can focus its compute resources on fulfilling the requests from clients
API Gateway
- An API Gateway is basically a reverse proxy that sits in front of all the microservices.
- It can act like a load balancer, distributing incoming requests across multiple instances of a service for better scalability and reliability.
Middleware
API Gateway uses middleware to offload common features from the backend services, like request validation, authentication, rate limiting, and logging. his helps each microservice stay focused on its own business logic instead of repeating these cross-cutting concerns.
API versioning and staging
So older API versions can still route to older microservice sets without breaking existing clients.
Protocol translation
Single unified endpoint for clients to access all backend services
This is especially valuable in a microservices architecture, where each service lives at its own address and port which would otherwise be messy for clients to manage.
System design interviews
It is good to mention the API Gateway when discussing microservices (it shows you understand real-world patterns), but you don’t need to dive too deep into its internals unless the interviewer asks. A brief nod to its role like routing, middleware, protocol translation, and unified entry point is enough.
Ingress Service
- An architecture that take advantage of Benefits of Reverse Proxy (反向代理)
Example
Cloudflare’s Edge Servers as Layer 1 to have Protection Against DDoS and Cache Static Content.
Then API Gateway/Load Balancer as Layer 2 to perform Load Balancing and Handles SSL Termination.
Lastly, there is a fast connection connects Cloudflare’s Edge Servers & the API Gateway/Load Balancer to facilitate reliable and fast communication between the 2 layers
In this case, both Cloudflare’s Edge Servers and API Gateway/Load Balancer are reverse proxy
